What is worth supplementing during autumn and winter?

Published Oct. 28, 2025 12:08

As for environmental conditions, low temperatures and dry air (especially in winter) favor the survival and transmission of many viruses, which is why the highest probability of infection occurs during the fall and winter. This includes some gastrointestinal infections (such as rotavirus). In addition, heated, rarely aired apartments dry out the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, weakening their cleansing function and increasing susceptibility to infection. In winter, air quality in cities deteriorates more often (smog), which weakens the respiratory system.
- During autumn and winter, we also experience less outdoor activity and lower fluid intake, which further dries out the mucous membranes. In addition, we see changes in daily diet, which are associated with reduced availability of fresh fruits and vegetables. In addition, shorter days contribute significantly to a decrease in the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, which in children and adults can increase susceptibility to infections," explains Prof. Dr. Dr. n. pharm. Pawel Ramos, Head of the Department of Pharmaceutical Pharmacy at the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Sosnowiec at the Silesian Medical University.
The autumn period also sees the return of children to nurseries and kindergartens, which increases the risk of transmission of infections. Autumn and winter also see an exacerbation of chronic diseases: for example, atopic dermatitis (AD) due to dry air and the presence of mites.
- It is important to remember that the proper state and functioning of our immune system is influenced by rational nutrition. Malnutrition, caused by insufficient intake of vitamins and micronutrients mainly zinc and selenium, can impair the body's ability to support the innate immune response. Deficiencies as a result of malnutrition can cause problems with key cells in the fight against disease, such as leukocytes, T lymphocytes and NK cells, the Silesian University expert adds.
So what vitamins and ingredients are worth taking during the fall and winter?
Insufficient intake of vitamins and certain minerals disrupts the body's function, which most often results in lowered mood and more infections. To counteract this, it is worthwhile to provide the body with vitamins and other components that are important during this period:
Vitamin D (D3), which significantly affects the modulation of the immune system and mucosal function and immune response. Vitamin D stimulates the body's immune process after by affecting immune cells such as macrophages and monocytes, which translates into antimicrobial activity, as well as causes inhibition of excessive immune response, which occurs, for example, in the course of autoimmune or autoinflammatory diseases. This vitamin, especially during the fall and winter, should be supplemented by everyone. From infants (as recommended by the pediatrician), to people with low sun exposure, the elderly, the obese, those with absorption disorders, and pregnant women (after consultation).
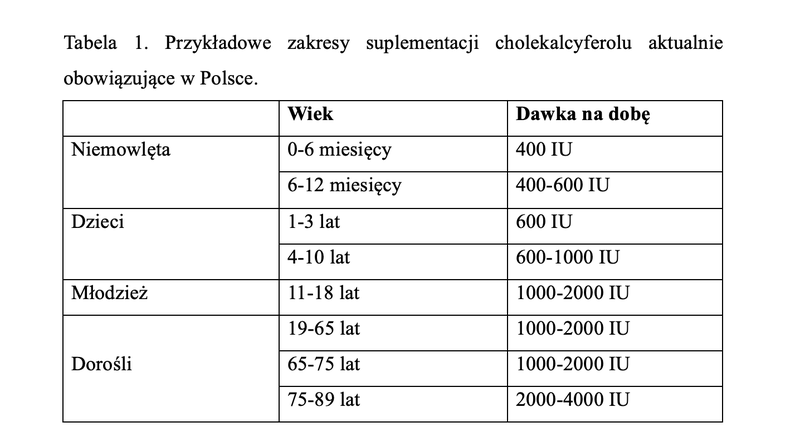
It is important to remember that in Poland only a small percentage of the population has sufficient vitamin D levels. However, like everything, vitamin D can also be overdosed. This is especially true for people who take it for a long time and in excessive doses. Symptoms of vitamin D overdose can be non-specific, such as emerging dermatitis, recurrent nausea and loss of appetite, as well as headaches and abdominal pain. In addition, some patients develop constipation, while others develop diarrhea. Effects of vitamin D overdose also include excessive sweating, hyperactivity, irritability, irregular heartbeat or a metallic taste in the mouth. Some people develop a rash after vitamin D (especially after large doses). Therefore, doses should be selected individually and laboratory determinations of its concentration in the body should be carried out during supplementation.
Vitamin C is primarily a powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals moreover, it supports leukocytes and the mucosal barrier; it can shorten the duration of infection when used in the initial phase. Sources of vitamin C are fresh vegetables and fruits (peppers, parsley, rosehips, black currants, kiwi, strawberries). It should be remembered that vitamin C is sensitive to processing: cooking, thawing and heating reduce its content, so it is best to eat raw products containing this vitamin. As for dosage, the requirement for adults is 75 to 90 mg per day. However, during periods of infection, higher doses (several hundred mg/day) can be used for short periods. People with kidney disease should exercise caution. It is worth remembering that the body excretes excess vitamin C in the urine, so during a period of infection it is better to take preparations containing vitamin C in smaller doses (e.g. 200mg) and more often, rather than taking large doses (e.g. 1000 mg) at a time. An alternative may also be extended-release preparations containing vitamin C, which release it gradually, which improves its absorption throughout the day.
Zinc is a key micronutrient necessary for the proper functioning of immune cells and the healing of mucous membranes. Zinc-containing preparations can shorten cold symptoms when taken early enough. The dosage of zinc varies and depends on whether one takes it short-term (10-25 mg of elemental zinc/day) or intends to take it long-term. Taking more than 40 mg/day can lead to copper and iron deficiency, resulting in anemia and other problems.
Vitamins A and E have supportive effects on mucous membranes, immune function and antioxidant properties. In addition, vitamin A (retinol/beta-carotene) is an important ingredient in ensuring proper vision and improving the appearance of the skin. Both vitamins act synergistically and protect the body from oxidative stress. Sources of vitamin A are animal products (liver, eggs, fish) and provitamin carotenoids in carrots, pumpkin, broccoli. In turn, sources of vitamin E are vegetable oils, nuts and seeds. It should be remembered that fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) have the ability to accumulate in the body, which poses a risk of overdose especially of vitamin A in pregnant women. Therefore, preparations containing these vitamins should be taken with caution.
B vitamins (especially B6) are involved in numerous enzymatic reactions, hemoglobin production, and antibody formation. In addition, vitamin B6 has an impact on the nervous system and immunity. Sources of B vitamins include meat, fish, whole grains, legumes. Caution should be exercised with vitamin B6 supplementation because with long-term intake of very high doses of B6 (e.g., >2 g/day) there is a risk of neuropathy manifested by numbness in the extremities and, in extreme cases, permanent nerve damage.
Selenium, iron, magnesium and other micronutrients are important for immune function their deficiencies worsen immunity. In addition, magnesium additionally supports proper sleep and reduces muscle tension. It should be noted that their supplementation is indicated with a confirmed deficiency through laboratory tests.
Probiotics affect the intestinal microbiota, which boosts the body's immunity after by strengthening the intestinal barrier, which is crucial for defense against pathogens, and modulate immune cell function and antibody production. By maintaining a healthy gut flora, probiotics prevent harmful substances from entering the body and can inhibit the development of bacterial, viral and fungal infections. They act as a natural protective shield, strengthening the body's local and general immunity. It is important to remember that the intestinal microbiome is variable and depends even on the latitude where the population is found. Therefore, it is important to choose probiotic preparations that contain tested strains of bacteria with scientifically proven effects. One of the best studied strains with documented effects in clinical practice are lactic acid bacteria from the genus Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Lactobacillus acidophilus LC1, Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFO 1748, Lactobacillus casei Shirota, Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 or Lactobacillus reuteri. When deciding on a probiotic, be sure to choose one with the correct number of CFU (colony forming units). This information should be on the package. Usually there are more than one billion colony-forming units per capsule. Preparations containing a lower number of CFUs are not able to effectively colonize the intestine, and their effects are short-lived. It is also important to pay attention to the storage conditions of probiotics. Many of them we need to store at refrigerator temperature, which ensures their proper survival.
Safety and prudence with supplements
Although supplements supplement the diet they cannot replace a healthy lifestyle of taking a balanced diet, adequate exercise and sleep, and vaccinations.
We should not abuse dietary supplements due to several aspects first and foremost, we should remember that dietary supplements are not subject to the same strict approval requirements as drugs. Therefore, if possible, we should choose a product registered as a drug also with OTC availability (that is, a drug that does not require a prescription). We should buy supplements from a reliable source, and that is an in-store pharmacy. It is important to remember that many supplements available on the Internet are adulterated and acquiring preparations through this route can endanger the health of patients. Pregnant women, nursing mothers, young children, people with chronic diseases and those taking chronic medications should consult a doctor or pharmacist each time before starting a new supplement. Many medications can interact with dietary supplements, which poses a danger to patients especially in cases of poly-pragmasy. It should also be remembered that substances in dietary supplements are easy to overdose on especially fat-soluble vitamins. Therefore, laboratory tests (e.g., vitamin D) help select a safe, personalized dose for each patient.
Practical tips for the autumn-winter season:
Performing vaccinations. It is important to remember that still influenza vaccination and other recommended vaccinations are one of the most effective methods of protection against disease.
Maintaining proper hygiene. Frequent hand washing, ventilating the premises, avoiding contact with sick people, and during epidemic periods, using protective masks effectively protects us from infection.
Adequate humidity. In order to reduce the incidence of infections during the autumn and winter, relative indoor humidity should be maintained at about. 40-60% (humidifiers, ventilation). This humidity range supports the mucous membranes and skin, which is especially important for patients suffering from atopic dermatitis.
Adequate diet and hydration of the body. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits (sources of vitamin C), oily fish (source of vitamin D3 and omega-3 acids), nuts and seeds (source of vitamin E and magnesium). These components affect the proper functioning of the immune system.
Outdoor activities. Unequivocally, walking and movement strengthen the body's immunity as long as they are adapted to the weather conditions especially when it comes to proper clothing.
In summary, the autumn-winter season is conducive to infections due to a number of factors: viral biology, deteriorated air quality and humidity, less sun exposure, poor winter diet and staying in clusters. The best protection is a combination of a healthy lifestyle (diet, sleep, exercise, hygiene, vaccinations), maintaining proper humidity and sensible supplementation - especially vitamin D, and if necessary also vitamin C, zinc, probiotics and other micronutrients preferably after consulting a doctor or pharmacist. In children, proper hydration, indoor ventilation and control of chronic diseases (such as AD) are additionally important.
Source: Silesian Medical University
Topics
witamina D / dieta / suplementacja / selen / odporność / bezpieczeństwo / higiena / probiotyki / witaminy z grupy B / Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny / infekcje / magnez / cynk / Paweł Ramos / wilgotność powietrza / witaminy A i E / okres jesienno-zimowy / mikroelementy / szczepienia / witamina C