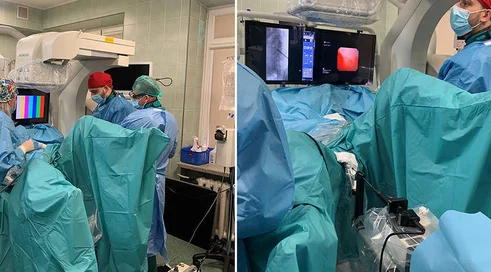
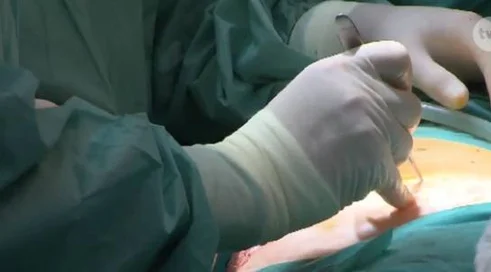
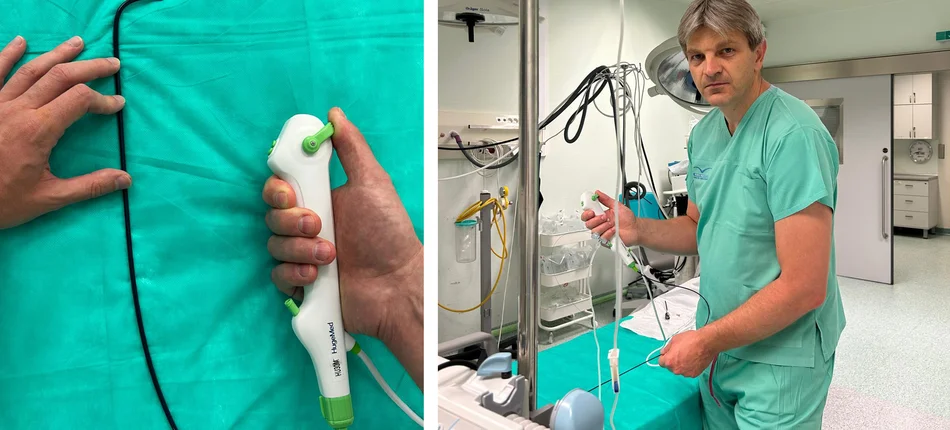
Mini-RIRS: New standard of treatment for kidney stones available in Poland

Published Dec. 20, 2024 08:50
Removing kidney stones is often a painful procedure. However, when they are smaller than 2.0 cm, they can be gotten rid of with a less painful ureteroscopic method, which is the RIRS procedure. This is a minimally invasive procedure in which stones are broken into smaller fragments using a laser inserted into the ureter using a flexible endoscope. The crushed deposits are expelled from the body along with the urine.
However, in about 25-30 percent of patients, due to the small diameter of the ureter, it is necessary to place a catheter before surgery to dilate it. About 80 percent of patients, on the other hand, require catheterization after surgery, during the removal of deposits. Both before and after the procedure, the patient must be provided with a catheter for a period of about 2-3 weeks, which, however, is associated with considerable discomfort - pain, hematuria, frequent urination or pushing.
Elimination of these problems is provided by the mini-RIRS procedure, which is currently the most modern in canine urology. It uses an endoscope much thinner than that used in the classic RIRS method. It is only 2 mm in diameter , which allows it to be used in patients with a small diameter of the ureter, without the need to place a catheter before and after the procedure. As a result, in addition to avoiding the need for catheterization, the patient has a shorter hospitalization and a faster recovery.
The first European to put mini-RIRS into practice was Dr. Marek Zawadzki, head of the urology department at St. Anne's Hospital in Piaseczno and co-founder of the Polish Center for Advanced Urology URO.pl. The occasion was this year's Congress of the Chinese Urological Society in Tianjin. As a result, the method is already being used at Piaseczno's St. Anne's Hospital. In turn, its patients are the first, and so far the only, people in Poland to be treated for kidney stones using the ultra-thin ureteroscope. - Mini-RIRS opens up entirely new possibilities in the treatment of kidney stones. The ultra-thin endoscope is a tool that allows for even greater precision and safety, which translates directly into patient comfort, says Dr. Marek Zawadzki. This is another step toward the urology of the future," he emphasizes.
Nephrolithiasis: Causes, symptoms and stages
Nephrolithiasis is one of the most commonly diagnosed diseases of the urinary system. It is estimated to affect about 10 percent of the population. Every year, tens of thousands of people in Poland require medical intervention due to an advanced form of this disease.
It involves the formation of deposits (called stones) in the urinary tract, mainly in the kidneys. These stones are caused by an excess of minerals in the urine, which crystallize and form hard deposits. Causes include a diet high in sodium, oxalates or protein, not drinking enough water. Genetic predisposition, as well as metabolic diseases such as diabetes, gout or hyperparathyroidism also contribute to the formation of deposits in the kidneys.
Nephrolithiasis occurs in people of all ages, but most often affects people between the ages of 30 and 50. Men are more often affected than women.
Disease stages:
- Asymptomatic deposits - small stones that do not cause complaints.
- Kidney colic attack - severe pain caused by the movement of a stone in the urinary tract.
- Blockage of the ureter - leads to hydronephrosis or urinary tract infection.
- Kidney damage - chronic blockage of urine outflow can lead to kidney failure.
Untreated kidney stones can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Hydronephrosis - enlargement of the kidney caused by blockage of urine outflow.
- Chronic renal failure - permanent kidney damage leading to the need for dialysis.
- Infections - can develop in blocked urinary tract, leading to sepsis.
The method of treatment depends on the size of the deposits
Traditionally, kidney stones - in the case of small stones - are treated by using pharmacotherapy to dissolve the deposits. Also effective for small deposits is breaking them up using sound waves or laser (RIRS). In contrast, for large stones, methods such as PCNL (percutaneous nephrolithotripsy, which requires a tissue incision) or mini-PCNL (the incision is smaller, and the shattered deposits are removed externally with an endoscope through the ureter) are used today. In particularly difficult cases, advanced surgical technology with combined techniques like ECIRS ( a combination of mini PCNL and RIRS) and occasionally the Da Vinci robot are used to remove deposits. The latest innovation, however, is mini-RIRS: a minimally invasive method using ultra-thin endoscopic tools.
New quality in kidney stone removal
The endoscopic, minimally invasive Mini-RIRS procedure allows the removal of kidney stones through the urinary tract. Using an endoscope with a diameter of just 2 mm, it is possible to precisely remove deposits even from hard-to-reach areas of the kidney. This is done without incising the skin, which significantly reduces the patient's hospitalization and recovery time.
Mini-RIRS is a method that is characterized by:
- Minimal invasiveness. No skin incisions reduce the risk of infection and postoperative pain.
- Quick recovery. Patients can return to daily activities just a few days after the procedure.
- Precision. The ultra-thin endoscope provides excellent visibility and allows removal of stones from hard-to-reach areas of the kidney.
- Application in a wide spectrum of diseases. Mini-RIRS is used not only in the treatment of kidney stones, but also in the diagnosis and treatment of other pathologies of the urinary system.
The method is particularly recommended for patients with:
- kidney stones that cannot be removed by traditional methods.
- Complications associated with kidney stones, such as hydronephrosis.
- diseases that require precise diagnosis and treatment within the urinary tract.
Mini-RIRS is the new standard in the treatment of urinary tract diseases. In addition to this method, patients at URO.pl in Piaseczno undergo, among other things, laser prostate treatments (HoLEP / ThufLEP/ ThuLEP ) and urological robotic surgeries using the 4th generation Da Vinci robot.
infra
Topics
kamica nerkowa